Despite its high calorie content even skimmed, this dairy product is actively used in dietary nutrition. It can be consumed by children and pregnant women. Lots of bodybuilders can’t imagine training without it as it helps build muscle mass. With such characteristics, it seems that cottage cheese is an ideal option for weight loss, but here some nuances should be known as well.
Mechanism of weight loss

Cottage cheese can become the main or an additional product for fasting programs, mono-diets, and long-term diets. It is also included in the diet of athletes on training days to speed up muscle building against the background of active fat burning. This is possible due to its useful properties:
- helps preserve muscle mass;
- speeds up metabolism;
- enriches the body with calcium;
- satisfies hunger for a long time;
- improves digestion;
- is a diuretic, helps get rid of excess fluid and swelling;
- provides the body with additional energy;
- combats compulsive overeating, as it has a beneficial effect on the nervous system: calms, improves mood, and removes irritability;
- has lipotropic properties and speeds up fat metabolism.
Nutritionists state that even just adding this product to a healthy diet helps maintain a figure without resorting to diets.
About the name. Translated from Old Slavonic, “tvorog” (cottage cheese) means “solid milk”.
Useful properties
It has been used to treat various diseases for a long time, so while losing weight you can improve your well-being and health at the same time. Its regular consumption:
- reduces the risk of cavities and fractures;
- activates brain activity, increases concentration, and improves endurance;
- improves vision;
- lowers cholesterol levels;
- promotes increased production of growth hormones;
- prevents anemia as it increases the hemoglobin level in the blood;
- in men, it improves conception ability by increasing the testosterone level.
Cottage cheese is one of the richest sources of protein available for digestion, that’s why it’s an easily digestible product. Much less hydrochloric acid, gastric juice, and enzymes are released for its digestion than in the case of milk. It is included in the dietary nutrition for the treatment of hypertension and atherosclerosis, heart and liver diseases.
Important. Cottage cheese is a rich source of protein and calcium, but it contains few vitamins.
Contraindications
Losing weight with cottage cheese implies its consumption in large quantities for a long period of time. If you have certain diseases, this can lead to health problems. Therefore, you need to know and follow the contraindications for such fasting:
- allergy;
- liver and kidney diseases;
- increased acidity of the stomach;
- digestive disorders;
- cardiovascular diseases.
All the above-mentioned diseases can aggravate if you consume cottage cheese for a long period of time, as well as cause flatulence, pain in the epigastric region, stool disorders, and flatulence.
Warning. Doctors warn that if you eat more than 200 g of cottage cheese per day, the salt balance in the body may be disturbed.
Types
By production method
1. Traditional
It can be the following types:
- Acidic
It is made from skim milk. Protein coagulation occurs under the influence of lactic acid formed as a result of lactic acid fermentation when sourdough is added to milk.
- Acid-rennet
Pepsin (rennet enzyme) and lactic acid bacteria sourdough are used simultaneously to coagulate protein.
2. Separated
Purified milk is separated to produce:
- skimmed milk;
- cream with a fat content of up to 55%.
Acid-rennet proteins are used for thickening. Skimmed cottage cheese is produced from milk, cooled, and then mixed with cream.
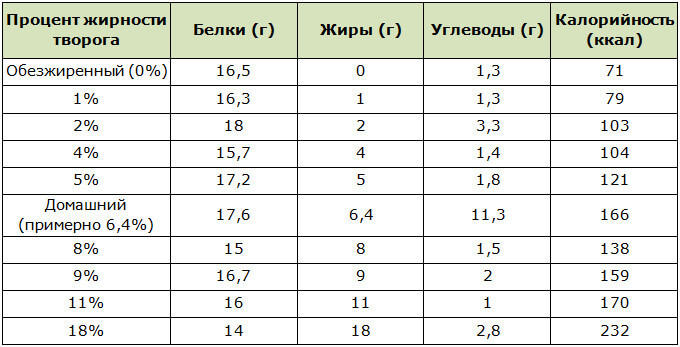
By fat content
- Fatty (more than 18%);
- classic (4-18%);
- semi-fat/low-fat (1-4%);
- skimmed/dietary (0%).
Other types
- With additives (raisins, dried fruits, nuts, candied fruits);
- calcined;
- grained – produced from cream and table salt;
- dietary – from skim milk, citric acid solution, sourdough and calcium chloride;
- table – from buttermilk and skim milk, produced in the form of curds, sweet mass, creams, cakes (high-calorie, not suitable for weight loss);
- albumin – from whey, but it is based not on casein, but on whey protein (albumin);
- home-made – from pasteurized or raw milk, without stabilizers or foreign substances.
Depending on its origin, it can be cow’s (traditional), goat’s (very useful) and sheep’s (has an unusual taste).
Interesting fact. 10 liters of milk are needed to produce just 1.5 kg of cottage cheese.
How to choose

It is better to buy this product in a transparent package (in order to see it) or by weight.
Signs of a quality product:
- milky white shade;
- crumbly, grainy consistency (if it is uniform, most likely harmful palm oil was used in production);
- unobtrusive smell of milk or yeast;
- slightly sour taste (but not sweet or pronounced sour);
- leaves an oily residue on fingers;
- intact packaging;
- pay attention to the production date and expiration date.
Signs of low quality:
- yellow, uneven color, blue and greenish spots indicate the presence of mold;
- too grainy consistency, when grains are hard and dry, or, on the contrary, excessively liquid;
- bitter taste;
- lack of milk smell;
- does not leave a mark on fingers;
- has been defrosted;
- contains many additional ingredients;
- damage and swelling of the package;
- expired or about to expire shelf life;
- a suspiciously low price may indicate the presence of soy, vegetable fats and other cheap ingredients;
- the presence of starch can be detected only at home by dripping iodine on the curd mass (it will turn blue).
Which type of cottage cheese is best for weight loss?
From industrial products for weight loss, skimmed cottage cheese is considered ideal: it does not contain fat and has the lowest calorie content. It is included in many diets.
If you prefer using natural products, make cottage cheese at home. This way you can be sure that there are no harmful impurities. However, in this case, you will have to sacrifice calorie content and fat content, high levels of which may not fit in your weight loss program.
Goat’s milk contains more calcium, but it is rarely skimmed and has a high calorie content (about 160 kcal), that’s why cow’s milk is a better option.
Be careful. Cottage cheese is an ideal environment for the development of pathogens. If you
Click to rate this post![Total: 0 Average: 0]



